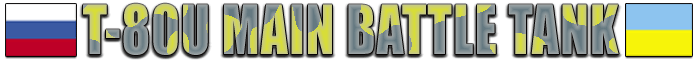Russian T-80U/UM/UM1/UM2 Main Battle Tank. Introduction: The development of the T-80 Main Battle Tank started in the Soviet era, with the tank entering service in 1976. The T-80 was the first production tank in the world to be equipped with a gas turbine engine. At first, Western analysts confused it with the T-72, as they looked similar, but actually the two tanks were rather different.
Actually, the two tanks were the product of two different design bureaus: the T-80 from Kharkiv Morozov Machine Building Design Bureau in Kharkiv, Ukraine, and the T-72 from Uralvagonzavod (Dzierzhinsky Ural Railroad Car Works) - UVZ, at Nizhny Tagil, Russia). They were only similar in general appearance.
The T-80 was a direct descendant of the earlier T-64, which was a high-technology main battle tank designed by the Tank Design Bureau of Kharkiv that went to revolutionize the Soviet tank concept. This new tank design concepts, were developed under the leadership of Aleksandr A. Morozov, and the T-64 became the first main battle tank of the new generation of Soviet-designed tanks. The T-64 was the first tank in the world to feature an automatic loader, enabling the crew to be cut from four to three - commander, gunner and driver. The T-64 is thus considered to be a landmark in the history of tank development in the Soviet Union, as every tank of the Soviet T-series entering service ever since (specially the T-80, T-80U, and its posterior developments) was influenced by the concepts initially introduced by the T-64 tank design. Unlike the T-72, the T-64 was only used by the Soviet Army and never exported. It was superior to the T-72 in most qualitative terms, until the introduction of the T-72B model in 1985. Both tanks armed elite and regular formations in Eastern Europe and elsewhere, the T-64A model being first deployed with East Germany's Group of Soviet Forces in Germany (GSFG) in 1976, and some time later in Hungary's Southern Group of Forces (SFG). By 1981 the T-64B began to be deployed in East Germany and later in Hungary. While it was believed that the T-64 was only reserved for elite units, it was also used by much lower "non-ready formations", for example, the Odessa Military District's 14th Army. The T-72 shared a similar destiny, being deployed on high readiness formation all across the Western Military District (Rogachev Guards Motorized Rifle Division in the Belarus MD and Iron Division's Motorized Rifle Division in the Carpathian MD) and Eastern Europe (Central Group of Forces in Czechoslovakia), but also on lower readiness formations on Transbaikal and Central-Asia MD since late 1980s. The T-64A was a further development of the T-64 tank by means of fitting it with a 125mm smoothbore gun (1969), improvement of the engine systems and running gear. The T-64B was a further development of the T-64A tank by means of installing a more advanced fire control system and armament stabilizer, guided missile system, improving the protection level etc. The T-64BV had all of those, plus featured an enhanced anti-radiation protection and add-on explosive reactive armor.
Other advanced features included a sophisticated multi-layer protection, NBC protection system, new layout of the power pack compartment, as well as the more sophisticated automatic fire control and gun-lunched missile ability that appeared with the T-64B in 1976. All those innovations were also installed on the T-80, as well as the high cost composite armor. This pattern continued with the T-80. The Morozov bureau improved upon the earlier design, introducing a gas turbine engine, developing 1,000 hp, in the original model. This gave the tank a high power-to-weight ratio and made it one of the most mobile main battle tanks in the world, and consequently it was referred to as the "flying tank". In subsequent variants of the T-80, the gas turbine has been replaced with a diesel engine, to lower maintenance costs. Between 1976 and the present the T-80 has undergone a number of modifications that included the T-80, T-80B, T-80U ("U" corresponds to "Y" in the cyrillic alphabet, meaning improved), and the T-80UD ("D" meaning diesel engine).
T-80U MBT The T-80 appeared as production model in 1984, retaining the basic features of the T-64 series (including the 125mm smoothbore gun with autoloader). Major innovations included the first Soviet use of a gas turbine engine, providing increased speed and power, and the first use of a laser rangefinder providing major improvements in fire control. It incorporates features common to both the T-64 and T-72, especially in weaponry. Easily distinguishable features of this tank as compared with the standard T-72 are the attachment of side skirts and twelve turret-mounted grenade launchers with seven on the left side and five on the right side. Firepower The T-80U(M) was also the first production Soviet tank to incorporate a laser range finder and ballistic computer system. The original night sight is the II Buran-PA (800-1300 meters range). The 12.7-mm MG NSVT has both remote electronically operated sight PZU-5 and gun-mounted K10-T reflex sight. The night sight cannot be used to launch the ATGM. The day sight can be used at night for launching ATGMs if the target is illuminated. A variety of thermal sights is available, including the Russian Agava-2, French SAGEM-produced ALIS and Namut sight from Peleng. Thermal sights are available for installation which permit night launch of ATGMs. The T-80U carries the 9M119 Refleks (NATO designation AT-11 Sniper) anti-tank guided missile system which is fired from the main gun. The range of the missile is 100m to 4,000m. The system is intended to engage tanks fitted with ERA (Explosive Reactive Armour) as well as low-flying air targets such as helicopters, at a range of up to 5km. The missile system fires either the 9M119 or 9M119M missiles, which have semi-automatic laser beam riding guidance.
The T-80U (and subsequent models) uses the 125mm 2A46M-1/2A46M-4 smoothbore 125 mm guns, though the fire control system is an improvement over that fitted to earlier Soviet tanks. The 125 mm weapon fires APFSDS, HEAT, and HEF ammunition, carrying 45 rounds (of which 28 stored in a carousel auto-loader), to a maximum aimed range of 3,000 - 4,000 meters (depending on the type of ammunition), at a rate of between 6 and 8 rounds/minute. Loading is hydro-mechanical with a 28 round carousel container. 45 rounds are carried. The gun fires separate loading projectiles which have semi-combustible cartridge case and sabot. The 125 mm gun is also capable of launching the 9M119M "Refleks-M" (AT-11 Sniper-B) ATGM, up to a range of 5,000 meters. Protection The T-80U has advanced composite armor at the front and sides, and the front, side and top armor behind Kontakt-5 ERA (T-80U, U(M), UK) or Arena APS (T-80UM1). Modernization options for the T-80U MBT - of which the best known example is T-80UM1 "Bars" (Snow Leopard) - include the fitting of the Arena prototype APS, Shtora-1 EOCMDAS or its components, upgraded 2A46-M4 main gun, GTD-1250G engine, and an air conditioner.
Kontakt-5 is a Russian type of third-generation explosive reactive armour. It is the first type of ERA which is effectively able to defeat modern APFSDS rounds. Introduced on the T-80U tank in 1985, Kontakt-5 is made up of "bricks" of explosive sandwiched between two metal plates. The plates are arranged in such a way as to move sideways rapidly when the explosive detonates. This will force an incoming KE-penetrator or shaped charge jet to cut through more armour than the thickness of the plating itself, since "new" plating is constantly fed into the penetrating body. A KE-penetrator will also be subjected to powerful sideways forces, which might be large enough to cut the rod into two or more pieces. This will significantly reduce the penetrating capabilities of the penetrator, since the penetrating force will be dissipated over a larger volume of armor. Other countermeasures include quieter running, gas-turbine engine which exhausts smokeless gases, improved heat insulation of roof and hatches, ventilation of the engine-transmission system, cooling system, smoke-laying system and smoke discharging system. Mobility The T-80 was the first Soviet operational tank to be powered by a gas-turbine, with a GTD-1000 gas-turbine engine developing 1100 hp. The road wheel spacing is not identical, with distinct gaps between the three pairs of road wheels. To extend the operational range of the T-80, additional fuel tanks can be mounted at the hull rear, which can be quickly jettisoned if required. A large circular container mounted on the turret rear carries two snorkels for deep fording operations. The larger one provides an air intake for the gas-turbine, with the other being fitted onto the radiator grill.
The T-80U MBT uses the GTD-1250 gas turbine. It is a step ahead of the GTD-1000T and GTD-1000TF engines that were installed on the previous tanks of T-80 line. This gas turbine can use jet fuels as well as diesel and low-octane gasoline, has good dynamic stability, service life, and reliability. the GTD-1250 gas turbine has a built-in automatic system of dust deposits removal. The latest engine - GTD-1250G - also features a hydro volume turning mechanism that reduces the fuel consumption by 9% while increasing the average speed by 29%. T-80UK - Command Tank The T-80UK tank provides command and control capability for field commanders and enable communications with superior command. It is similar to the T-80U but has a number of additional features. It is fitted with the Shtora-1 countermeasures suite also fitted on the T-90 tank. Shtora-1 is produced by Electronintorg of Russia. This system includes infrared jammer, laser warning system, grenade discharging system and a computerized control system. Operational range is 200m. The tank has a combined symmetric dipole antenna for both UHF and HF communications. This increases range when the tank is stationary - up to 40km for the R-163-50U radio and 350 km for the R-163-50K radio. An AB-1-P28 1kW benzene generator is provided to power communications when the tank is stationary. T-80UK also has a more advanced fire control system, automatic loader for the gun, built-in turret ERA (Explosive Reactive Armour) and TNA-4-3 navigational aid. Specifications
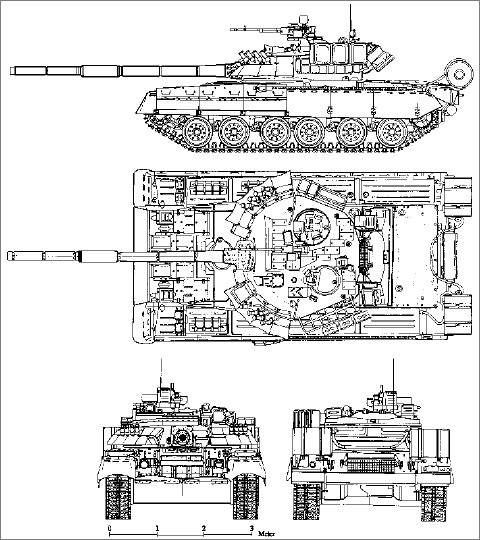
Ukrainian T-80UD, T-84 Oplot, and T-84 Yatagan MBT.
T-80UD Main Battle Tank The T-80UD main battle tank was designed by the Kharkiv Morozov Machine Building Design Bureau - KMBD at the beginning of the 1980's and entered series production at the State Enterprise Malyshev Plant in 1985. KMBD is a state-owned company settled in Kharkiv, Ukraine, which designed many of the most famous Soviet tanks during the course of it's history. It was responsible for many important Soviet tanks, including BT tank series, T-34, T-55, and T-64. Later, the company has produced advanced, quality designs following the T-64 heritage, like the T-80 and it's variants, and more recently, the T-84 series of Main Battle Tanks. Firepower: The T-80UD is fitted with an advanced fire control system, and either the gunner or commander can lay and fire the main armament at stationary and moving targets while the tank is stationary or moving with a high first round hit probability. The commander's PNK-4S observation and sighting system comprises a commander's TKN-4S combined day/night sight and a gun position sensor. The commander's TKN-4S combined sight is stabilized in the vertical plane and has three channels: a day unity vision channel, a day channel with magnification of x8 and a night channel with magnification of 5.4x. The gunner's 1G46 day sight has a two-axis stabilized line of sight and incorporates a laser range-finder and a missile guidance capability. In the standard version the gunner has a TO1-KO1E sighting system with TPN-4E image intensification sight, but as an option, the Buran-Catherine-E thermal imaging sight can be fitted. The 1V528-1 ballistic computer automatically takes into account all the inputs from the sensors including tank speed, angular target speed, gun trunnion axis cant, crosswind speed, target range, and course angle. Additionally, the following parameters are manually input: ambient air temperature, charge temperature, barrel wear ambient air pressure and so on. The computer also computes the time when the high-explosive fragmentation projectile with controlled detonation should be detonated over the target. The main armament consists of a 125mm KBA3 smoothbore gun fed by a carousel-type automatic loader and fitted with a thermal sleeve and fume extractor (bore evacuator). The main gun has a quick-replacement barrel which can be changed under field conditions without the need to remove the gun from the tank. This gun is installed in the KMBD's main battle tanks T-84 Oplot and T-80UD. The gun weighs 2500 kg, and has a muzzle velocity of 1700 m/s, when firing firing the 3VBM17 "MANGO" APFSDS round. T-80UD carries 45 two-piece rounds (projectile and charge), of which 28 rounds are placed in the automatic loader, with the remainder being stored at the driver's station and in the fighting compartment. Types of ammunition that can be fired by the gun include APFSDS (armor-piercing stabilized discarding sabot), HEAT (high explosive anti-tank), HE-FRAG (high explosive fragmentation) rounds and the 9M119M "Refleks-M" (AT-11 Sniper-B). The role of the 9M119M "Refleks-M" system is to enable the main gun to fire a laser guided missile with a maximum range of 5,000 m. The missile consists of two parts. The missile can be fired while both the tank and target are moving. The tandem warhead enables the missile to defeat targets fitted with explosive reactive armor with a high degree of efficiency. Although the primary role of the missile is to engage tanks and other AFV's operating at ranges beyond the effective range of the 125mm tank gun firing conventional ammunition, it can also be fired against other battlefield targets such as hovering helicopters and pillboxes. Besides the main gun, the T-80UD also has a 7.62mm coaxial machine gun and 12.7mm anti-aircraft machine gun. The anti-aircraft machine gun is mounted on the commander's cupola and is intended for use in the ground/air and ground/ground roles being aimed and fired while remaining in the vehicle under full armor protection from the commander's station. The machine gun can be elevated from -5° to +70° and traversed through +/-75° to the right and left of the vehicle longitudinal axis, or through +360° together with the tank turret. The machine gun is fitted with a vertical stabilization system providing stabilization in the vertical angle range of -3° to +20°. Protection:
The armor protection of the T-80UD, which includes advanced multi-layer armor and explosive reactive armor package for the turret and chassis, provides to the T-80UD a high level of battlefield survivability. The T-80UD can disguise itself on the battlefield by laying a smoke/aerosol screen. Mounted on either side of the turret is a bank of four electrically operated smoke grenade launchers.
The T-80UD can lay its own smoke screen by injecting diesel fuel in the engine exhaust (i.e. by using so-called engine smoke emitter). To reduce the thermal signature of the tank on the battlefield, the T-80UD power pack compartment top deck is fitted with special heat insulation. Mobility: The T-80UD is powered by a model 6TD-1 6-cylinder diesel engine developing 1,000 hp. The air inlet of the engine allows air to be ducted from the least dusty quarter and enables water obstacles to be crossed to a water depth of 1.8 m without preparation. There are two parts to the air filtration system, the centrifugal pre-cleaners and the air cleaner casing. This enables the tank to be operated in hot and dusty conditions for up to 1,000 km without a change of filters and to carry out combat under radioactive conditions. The suspension is of the torsion bar type with each side having six dual rubber-tyred road wheels with the idler at the front, drive sprocket at the rear and track support rollers. The upper part of the suspension is covered by a skirt, the forward part of which is armored (fitted with explosive reactive armor). A rubber mat hangs at the front of the vehicle and this helps to keep the dust down. Other Features:
The T-80UD MBT standard equipment also includes an NBC system, provision for deep fording, fire detection/suppression system, radiation shielding and a dozer blade mounted under the front of the hull. The NBC protection system protects the crew and inner equipment of the tank against the effects of nuclear explosions, radioactive dust, toxic agents and bacteriological materials. The deep fording equipment enables the tank to cross water obstacles to a water depth of 5 m (1.8 m deep water obstacles can be crossed without preparation). The fire detection/suppression system enables internal fires to be detected and suppressed in both crew compartment and power pack compartment. The radiation shielding is designed in the form of liner fixed on both internal and external surfaces of the tank. The dozer blade enables the tank to dig up a tank caponier within 15-40 minutes depending on the type of ground. The T-80UD can be fitted with various types of mine-clearing system at the front of the hull including KMT-6 plough-type system and KMT-7 roller-type system. Two long-range fuel tanks and an unditching beam can be mounted at the rear of the hull. The T-80UD main battle tank is in service with Ukraine, Russia and Pakistan.
T-84 Oplot Main Battle Tank The first T-84 prototype was completed in 1994, and then several other prototypes were produced. Those were subjected to extensive trials, both in the Kharkiv Morozov Machine Building Design Bureau facilities and with the Army. Only after successful completion of this extensive trials program in mid-1990's, the T-84 entered service with the Ukrainian Army in 1999. The T-84 Oplot main battle tank is the result of the continued main battle tank development by the Kharkiv Morozov Machine Building Design Bureau, which is Ukraine's leading design authority for armored fighting vehicles. The overall layout of the T-84 Oplot main battle tank is conventional, with the driver's compartment at the front, fighting compartment in the center and power pack at the rear. The driver is seated in the center and has a single-piece hatch cover that lifts and swings to the right. In front of this are three forward-facing periscopes, and the center one of those can be replaced by a night driving device. There is an escape hatch in the hull floor, behind the driver. The commander is seated on the right and the gunner on the left. Both are provided with single-piece roof hatches. The T-84 Oplot main battle tank is based on the T-80UD, but has a number of advanced features which distinguish it from the former:
The T-84 Oplot main battle tank is a very efficient fighting machine intended to fulfil the mission of providing mobile protected firepower in all types of terrain, is very well protected, has good battlefield mobility as well as good strategic mobility, and is able to undertake a wide range of battlefield missions on a 24 hour basis under all weather conditions. 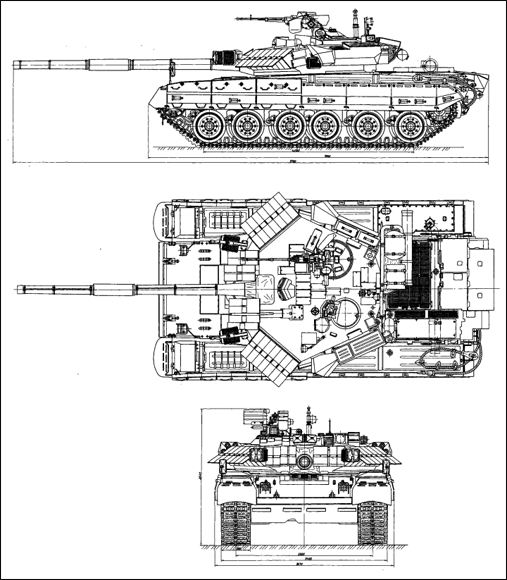
T-84 Yatagan MBT The T-84 Yatagan (also referred to as the KERN2-120 - the designation of the prototype - or the T-84-120) main battle tank is based on the T-84 Oplot MBT, incorporating new technical solutions that were developed during modernization of T-72-120 Main Battle Tank. Both are products of the Kharkiv Morozov Machine Building Design Bureau of Kharkiv, Ukraine. The T-84 Yatagan Main Battle Tank is fitted with a fire control system derived from the T-84 Oplot MBT and adapted to the new armament. Its main specific feature is a 120mm smoothbore gun with a chrome plated barrel, which is NATO standard ammunition compatible, and has the ability to fire a barrel-launched 120mm guided missile, designed and manufactured in Ukraine. The T-84 Yatagan main battle tank is fitted with a fire control system derived from the T-84 Oplot MBT and adapted for the new armament. The protection levels of this main battle tank are also the same as the T-84 Oplot MBT, as well as where the mobility characteristics are concerned.
T-84 Yatagan MBT Specifications
Sources: Vasily Fofanov's Modern Russian Armour Page Kharkiv Morozov Machine Building Design Bureau - KMBD Uralvagonzavod (Dzierzhinsky Ural Railroad Car Works) - UVZ The ARMOR Site! is © Copyright 1997-2006 Fabio Prado . All Rights Reserved. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||